You need enough money to cover your expensesuntil you get your next paycheck. Once you receive that paycheck,you can repay the lender the amount you borrowed, plus a littleextra for the lender’s assistance. Notes payable and accounts payable are both liability accounts that deal with borrowed funds. Many of us get confused about why there is a need to record notes payable. Some people argue that notes payable can be adjusted under the head of account payables.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
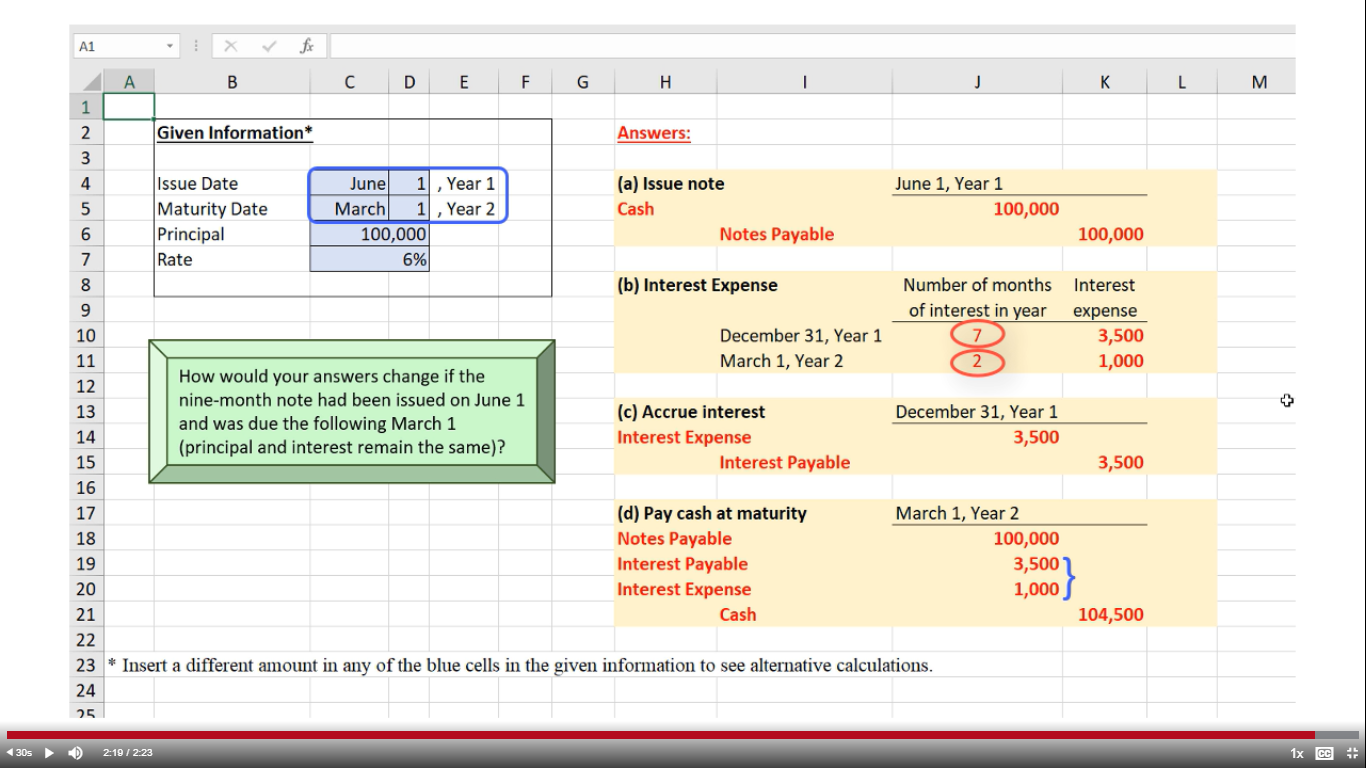
The principal of $10,475 due at the end of year 4—within one year—is current. The principal of $10,999 due at the end of year 5 is classified as long term. In the following example, a company issues a 60-day, 12% interest-bearing note for $1,000 to a bank on January 1.
How to Calculate Gross Profit: A Simple Guide for Business Owners
However, the nature of liability depends on the amount, terms of payments, etc. For instance, a bank loan to be paid back in 3 years can be recorded by issuing a note payable. The nature of note payable as long-term or short-term liability entirely depends on the terms of payment. As previously discussed, the difference between a short-term note and a long-term note is the length of time to maturity.
Journal Entry to Record Equipment Purchased and Issuance of Notes Payable
Instead, the interest expense will be calculated for an exact period until the loan was paid. A note payable might be written if the debtor has failed to pay the promised amount on the due date. The account payable might be converted into a note payable on non-payment beyond the due date. Notes payable are most generally issued by the borrower or the lender when a bank loan is taken. When a company purchases bulk inventory from suppliers, acquire machinery, plant & equipment, or take a loan from a financial institution. Every company or business requires capital to fund the operations, acquire equipment, or launch a new product.
- There is an ebb and flow to business that can sometimes produce this same situation, where business expenses temporarily exceed revenues.
- In addition, the timeframe can differ hugely and range from a few months to five years or maybe more.
- In addition, the amount of interest charged is recorded as part of the initial journal entry as Interest Expense.
- The company owes $21,474 after this payment, which is $31,450 – $9,976.
- Therefore, in reality, there is an implied interest rate in this transaction because Ng will be paying $18,735 over the next 3 years for what it could have purchased immediately for $15,000.
- The date of receiving the money is the date that the company commits to the legal obligation that it has to fulfill in the future.
Recording Short-Term Notes Payable Created by a Loan

The premium or discount amount is to be amortized over the term of the note. He has a CPA license in the Philippines and a BS in Accountancy graduate at Silliman University. In the second case, the firm receives the same $5,000, but the note is written for $5,200.
Long-Term Notes Payable, Interest, and the Time Value of Money
The contracts must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), being identified as a security sometimes. Notes payable on the balance sheet take a spot under accrued interest vs regular interest the liabilities column. They are considered current liabilities when the amount is due within one year, and else they are recorded under the long-term liabilities category.
The interest of $200 (12% of $5,000 for 120 days) is included in the face of the note at the time it is issued but is deducted from the proceeds at the time the note is issued. Each year, the unamortized discount is reduced by the interest expense for the year. This treatment ensures that the interest element is accounted for separately from the cost of the asset. If neither of these amounts can be determined, the note should be recorded at its present value, using an appropriate interest rate for that type of note. This situation may occur when a seller, in order to make a detail appear more favorable, increases the list or cash price of an item but offers the buyer interest-free repayment terms. A problem does arise, however, when an obligation has no stated interest or the interest rate is substantially below the current rate for similar notes.
When you repay the loan, you’ll debit your Notes Payable account and credit your Cash account. For the interest that accrues, you’ll also need to record the amount in your Interest Expense and Interest Payable accounts. Let’s look at what entries are passed in the journal for notes payable. In addition, the amount of interest charged is recorded as part of the initial journal entry as Interest Expense.