
These investments help businesses maintain modern, efficient, and safe work environments, especially as they grow or modify operations. While they’re most definitely both considered part of the asset category, current assets and plant assets don’t share all that much in common. Later on, the company will charge the depreciation according to the method of depreciation it usually follows.
- The overall value of a company’s PP&E can range from very low to extremely high compared to its total assets.
- Vehicles include any company-owned cars, vans, trucks, or other transportation assets used for business purposes.
- Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life, reflecting wear and tear, aging, or obsolescence.
- Needless to say, they’re an enormously important part of producing goods and/or services in an economically efficient manner.
- Buildings are vital for housing employees, storing inventory, or hosting customers, and they may be repurposed or expanded as a business grows.
- A plant asset can be defined as any asset that can be utilized to produce revenue for the company.
Acquisition Costs

Purchases often signal that management expects long-term profitability of its company. Industries or businesses that require extensive fixed assets like PP&E are described as capital intensive. Current assets are expected to be used within a year or short-term time frame. Current assets typically include cash, inventory, accounts receivable, and other short-term liquid assets. In contrast, plant assets represent long-term property expected to be around for at least a year, often quite a bit longer than that. Though plant assets are sometimes seen as expensive, not all have the same value or are prioritized Bookkeeping for Chiropractors by a company.

Accounting for Plant Assets
- Plant assets usually require a significant financial investment due to their essential role and durability in operations.
- How do businesses decide when to replace a plant asset instead of repairing it?
- When a company acquires a plant asset, it capitalizes the asset’s cost on the balance sheet rather than expensing the purchase.
- Thus, for accounting and plant asset disposal, they are recorded at cost, and are depreciated over the estimated useful life, or the actual useful life, whichever is lower.
- Depreciation is the process by which a plant asset experiences wear and tear over a particular period of time.
- Machinery and equipment are typically among the highest-depreciating assets due to constant usage, which results in gradual wear and tear.
- Long-term investments, such as bonds and notes, are also considered noncurrent assets because a company usually holds these on its balance sheet for more than one fiscal year.
Land can be purchased by a start-up company for a single site, but a bigger company can possess several types of land that serve diverse functions for the company and its subsidiaries. Monte Garments is a QuickBooks factory that manufactures different types of readymade garments. The company also has a printing press for printing customized merchandise with brand designs. A new press technology has just launched in the market, and the company owner decided to acquire the machine. The cost of the machine is USD100,000, and it is expected to stay useful for five years with a residual value of USD10,000.
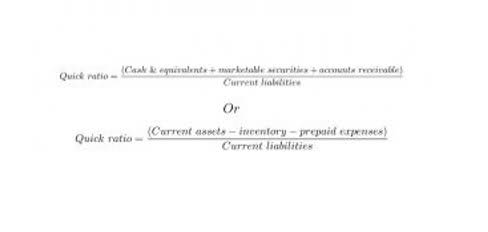
Improvements
When purchasing a building for retail operations, the historical cost could include the purchase price, transaction fees, and any improvements made to the building to bring it to use. Current assets are short-term assets like inventory and are likely to be converted into cash within one year. Since these assets produce benefits for more than one year, they are capitalized and reported on the balance sheet as a long-term asset. This means when what is plant assets a piece of equipment is purchased an expense isn’t immediately recorded.
Current assets versus plant assets
In the end, be careful to distinguish between asset types both on the balance sheet and in practice. Investments in plant can serve as a competitive advantage, allowing companies to produce superior products or deliver services more efficiently than competitors. Despite the fact that upgrades might be costly, they are nevertheless regarded an asset to a company since they constitute an additional investment in ensuring the company’s success. This is crucial to consider when buying land for a business since it might mean the difference between a long-term profit or loss.
- Depreciation is essential in reflecting the wear and tear of an asset, and it helps maintain accurate financial reporting.
- Current assets are expected to be used within a year or short-term time frame.
- Depending on the industry, plant assets may make up either a very substantial percentage of total assets, or they may make up only a small part.
- The IAS 16 of the IFRS governs the rules regarding recognizing and recording the plant assets in the company’s financial statements.
- Any land maintenance, improvement, renovations, or construction to increase building operations or revenue generation capacity are also recorded as part of the plant assets.
- Proper management, including timely upgrades and maintenance, is essential to maximize the benefits of these assets.